Image
Enhancement in Frequency Domain.
Find the 2D
discrete Fourier transform for given input images
1. Impulse
2. Rectangle
3. Sine
1.
Computing and Visualizing 2D
DFT for impulse image
clear
all;
close
all;
clc;
display('method of taking 2D DFT of impulse image')
f1
= imread('impulse.jpg');
%
f2 = im2bw(f1);
f
= imresize(f1,[512 512]);
F
= fft2(f);
s
= abs(F);
Fc
= fftshift(s);
s2
= log(1 + abs(Fc));
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(f);
title('Impulse Image');
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(s, []);
title('Fourier Spectrum of given image "can be seen
on four corners"');
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(abs(Fc), []);
title('Centered Fourier Spectrum of given image');
subplot(2,2,4);
imshow(s2, []);
title('Spectrum Visually enhanced by a log
trasformation');
Computing 2D DFT from both programming logic and direct inbuilt
function
clear
all;
close
all;
clc;
a
= imread('impulse.jpg');
a1
= imresize(a,[512 512])
s
= double(a1);
b
= size(s)
m
= b(1)
n
= b(2)
e
= 2.718
for u=0:1:m-1
for x=0:1:n-1
w1 = e.^(-j*2*pi*u*x/m);
w(u+1,x+1)=w1;
end
end
for i=1:1:b(1)
f11 = (w)*(s(i,:).');
f1(i,:)=f11;
end
for i=1:1:b(2)
f21 = (w)*(f1(:,i));
f2(:,i)=f21;
end
i2
= abs(f2);
g
= fft2(a1); %
computing direct 2D DFT of impulse image
g1
= abs(g);
subplot(2,2,1)
imshow(a);
title('Original Impulse image');
subplot(2,2,2)
imshow(a1);
title('Binary image of original
Impulse image');
subplot(2,2,3);colormap(gray);
imagesc(fftshift(log(1+i2)));
title('2D DFT(I2) of binary image by
programming');
subplot(2,2,4);colormap(gray);
imagesc(fftshift(log(1+g1)));title('2D DFT(G1) of binary image by inbuilt function');
Computing 2D inverse DFT of Previously generated 2D DFT of impulse
image.
clear
all;
close
all;
clc;
display('method of taking 2D inverse DFT of Sine image')
f1
= imread('impulse.jpg');
f
= imresize(f1,[512 512]);
F
= fft2(f);
s
= abs(F);
Fc
= fftshift(s);
s2
= log(1 + abs(Fc));
f12
= ifftshift(Fc);
f1
= ifft2(f12);
subplot(2,3,1);
imshow(f);
title('Original Impulse Image');
subplot(2,3,2);
imshow(s, []);
title('Fourier Spectrum of given image "can be seen
on four corners"');
subplot(2,3,3);
imshow(abs(Fc), []);
title('Centered Fourier Spectrum of given image');
subplot(2,3,4);
imshow(s2, []);
title('Spectrum Visually enhanced by a log
trasformation');
subplot(2,3,5);
imshow(abs(f12), []);
title('Back to Fourier spectrum');
subplot(2,3,6);
imshow(abs(f1), []);
title('inverse fourier transform');
2.
Computing and Visualizing 2D
DFT for Sine image
clear
all;
close
all;
clc;
display('method of taking 2D DFT of impulse image')
f1
= imread('sine2.gif');
f
= imresize(f1,[64 64]);
F
= fft2(f);
s
= abs(F);
Fc
= fftshift(s);
s2
= log(1 + abs(Fc));
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(f);
title('Original Sine Image');
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(s, []);
title('Fourier Spectrum of given image "can be seen
corners"');
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(abs(Fc), []);
title('Centered Fourier Spectrum of given image');
subplot(2,2,4);
imshow(s2, []);
title('Spectrum Visually enhanced by a log
trasformation');
Computing 2D DFT from both programming logic and direct inbuilt
function
clear
all;
close
all;
clc;
a
= imread('sine2.gif');
s1
= im2bw(a);
s12
= imresize(s1,[128 128]);
s
= double(s12);
b
= size(s)
m
= b(1)
n
= b(2)
e
= 2.718
for u=0:1:m-1
for x=0:1:n-1
w1 = e.^(-j*2*pi*u*x/m);
w(u+1,x+1)=w1;
end
end
for i=1:1:b(1)
f11 = (w)*(s(i,:).');
f1(i,:)=f11;
end
for i=1:1:b(2)
f21 = (w)*(f1(:,i));
f2(:,i)=f21;
end
g
= fft2(s);
g1
= abs(g);
i2
= abs(f2);
subplot(2,2,1)
imshow(a);
title('Original Sine image');
subplot(2,2,2)
imshow(s);
title('Binary image of original
image');
subplot(2,2,3)
colormap(gray);
imagesc(fftshift(log(1+i2)));
title('2D DFT of binary image by programming');
subplot(2,2,4)
colormap(gray);
imagesc(fftshift(log(1+g1)));
title('2D DFT of binary image by
direct')
Computing 2D inverse DFT of Previously generated 2D DFT of sine
image.
clear
all;
close
all;
clc;
display('method of taking 2D inverse DFT of Sine image')
f1
= imread('sine2.gif');
f
= imresize(f1,[64 64]);
F
= fft2(f);
s
= abs(F);
Fc
= fftshift(s);
s2
= log(1 + abs(Fc));
f12
= ifftshift(Fc);
f1
= ifft2(f12);
subplot(2,3,1);
imshow(f);
title('Sine Image');
subplot(2,3,2);
imshow(s, []);
title('Fourier Spectrum of given image "can be seen
on four corners"');
subplot(2,3,3);
imshow(abs(Fc), []);
title('Centered Fourier Spectrum of given image');
subplot(2,3,4);
imshow(s2, []);
title('Spectrum Visually enhanced by a log
trasformation');
subplot(2,3,5);
imshow(abs(f12), []);
title('Back to Fourier spectrum');
subplot(2,3,6);
imshow(abs(f1), []);
title('inverse fourier transform');
3.
Computing and Visualizing 2D
DFT for Rectangle image
clear
all;
close
all;
clc;
display('method of taking 2D DFT of rectangle image')
f1
= imread('rectangle.jpg');
f2
= im2bw(f1);
f = imresize(f2,[64 64]);
F = fft2(f);
s = abs(F);
Fc
= fftshift(s);
s2
= log(1 + abs(Fc));
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(f2);
title('Rectangle Original Image');
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(s, []);
title('Fourier Spectrum of given image "can be seen
on four corners"');
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(abs(Fc), []);
title('Centered Fourier Spectrum of given image');
subplot(2,2,4);
imshow(s2, []);
title('Spectrum Visually enhanced by a log trasformation');
Computing 2D DFT from both programming logic and direct inbuilt
function
clear
all;
close
all;
clc;
a
= imread('rectangle.jpg');
s1
= im2bw(a);
s12
= imresize(s1,[64 64]);
s
= double(s12);
b
= size(s)
m
= b(1)
n
= b(2)
e
= 2.718
for u=0:1:m-1
for x=0:1:n-1
w1 = e.^(-j*2*pi*u*x/m);
w(u+1,x+1)=w1;
end
end
for i=1:1:b(1)
f11 = (w)*(s(i,:).');
f1(i,:)=f11;
end
for i=1:1:b(2)
f2(:,i)=f21;
end
g
= fft2(s);
g1
= abs(g);
i2
= abs(f2);
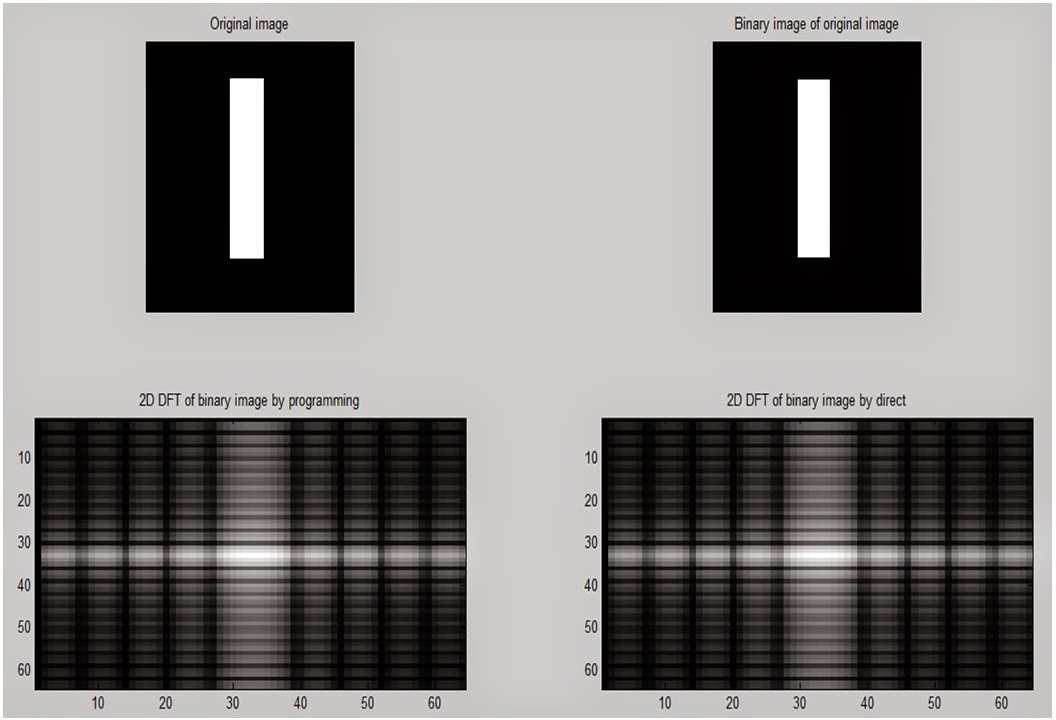
subplot(2,2,1)
imshow(a);
title('Original image');
subplot(2,2,2)
imshow(s);
title('Binary image of original
image');
subplot(2,2,3)
colormap(gray);
imagesc(fftshift(log(1+i2)));
title('2D DFT of binary image by
programming');
subplot(2,2,4)
colormap(gray);
imagesc(fftshift(log(1+g1)));
title('2D DFT of binary image by
direct')
Computing 2D inverse DFT of Previously generated 2D DFT of
rectangle image.
clear
all;
close
all;
clc;
display('method of taking 2D DFT of rectangle image')
f1
= imread('rectangle.jpg');
f2
= im2bw(f1);
f = imresize(f2,[64 64]);
F = fft2(f);
s = abs(F);
Fc
= fftshift(s);
s2
= log(1 + abs(Fc));
Fc1=
ifftshift(Fc);
F1
= ifft2(Fc1);
subplot(2,3,1);
imshow(f2);
title('Rectangle Original Image');
subplot(2,3,2);
imshow(s, []);
title('Fourier Spectrum of given image "can be seen
on four corners"');
subplot(2,3,3);
imshow(abs(Fc), []);
title('Centered Fourier Spectrum of given image');
subplot(2,3,4);
imshow(s2, []);
title('Spectrum Visually enhanced by a log
trasformation');
subplot(2,3,5);
imshow(abs(Fc1), []);
title('Back to Fourier Transform');
subplot(2,3,6);
imshow(abs(F1), []);
title('Inverse Fourier Transform');









No comments:
Post a Comment